Topics|Metering pump accessories Air Chambers
The many unique advantages of diaphragm pumps include outstanding quantitative consistency, generation of high pressure, no sliding parts, leak-free design, and idling capability. They have one fault, however: their operation generates pulsation.
Pulsation can lead to a variety of problems: it causes pipe vibration, requires costly thick pipes, and is difficult to accommodate in a continuous production process.
An air chamber is generally used to eliminate such pulsation.
What is an Air Chamber?

An air chamber is a pulsation-damping device. It reduces the pulsation of a reciprocating pump and contributes to stable liquid flow by utilizing the compressibility of the air in the chamber.
An air chamber can mitigate the various problems caused by pulsation, such as pipe vibration and the overfeed phenomenon.
Operation Principles
(1) When Pump Is in Evacuation Phase
- If the air in the air chamber dissolves into the liquid and decreases in volume, pulsation will result. Therefore, the air must be replenished periodically.
- An air chamber cannot be used with liquids affected by exposure to air.
- The throttle valve must be readjusted every time the discharge volume of the pump is changed.
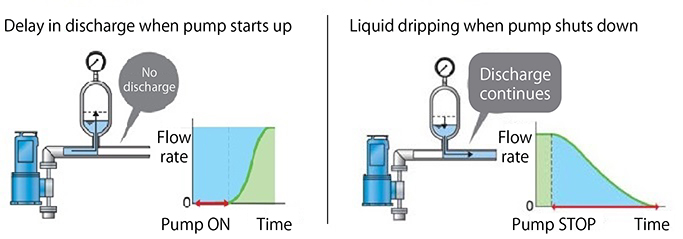
- Because it takes time for a sufficient amount of air to accumulate in the air chamber, it takes time for the liquid to be discharged (a discharge delay occurs when the pump is started).
- When the pump is shut down, the air accumulated in the air chamber pushes out the liquid, so liquid continues to be discharged until the pressure in the air chamber falls sufficiently (resulting in liquid dripping when the pump is shut down).
- Be sure to install a relief valve near the pump. Particularly when a cutoff valve is installed on the pipe, fully open it before turning on the pump.
- Be careful not to exceed the maximum operating pressure.
- Do not place pipes directly on the ground in cold areas. Keep pipes, pumps, and air chambers warm in locations where they are likely to freeze, such as the outdoors.
- Do not use an air chamber in direct sunlight. This is necessary to prevent abnormal temperature rise (in metal products) and to avoid the influence of ultraviolet rays (on PVC products).
- Eliminates the need for daily maintenance such as replenishment of the air chamber with air and pressure adjustment of the throttle valve.
- Reduces total cost thanks to reduced piping and less frequent maintenance.
- Continuous flow at a constant rate without pulsation results in more accurate flow rate control.
- Safety is improved.
Liquid more readily compress air in the air chamber than pass through a throttle valve.
Consequently, although liquid is discharged through the throttle valve, it also accumulates in the air chamber in proportion to the excess of pressure loss over the air pressure.
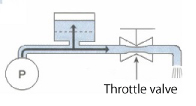
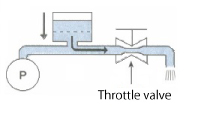
(2) When Pump Is in Intake Phase
Since no liquid is discharged from the pump, no pressure loss occurs on the throttle valve, as is the case in the evacuation process. Therefore, the liquid accumulated in the air chamber in (1) is discharged by compressed air.
Repetition of phases (1) and (2) generates a constant flow without pulsation downstream of the throttle valve.
Disadvantages of the Air Chamber
Installation Precautions
TACMINA's Pulsation-Damping Smoothflow Pump
TACMINA´s Smoothflow Pump reduces pulsation without incorporating an air chamber.
The lack of an air chamber brings the following benefits.